The Climate Crisis in Central America: Facts and How to Help

How is climate change affecting the region?
Climate change significantly impacts Central America, worsening many of the existing problems in the region, such as poverty, food insecurity, and environmental degradation, especially in the Central American Dry Corridor.
Seven Effects of Climate Change in Central America
- Less rain and higher temperatures
- Weather-related extreme events
- Unpredictable climate patterns and drought
- Displacement and social conflict
- Biodiversity at risk
- Health impact
- Economic impact
A climate change adaptation approach is necessary to mitigate these effects, including economic diversification, climate-resilient agriculture techniques, and infrastructure improvement to better deal with natural disasters.
Scroll down to learn more about these impacts and how you can help those in Central America who are feeling the effects of climate change.
MEDIA CONTACT
Robyn Fieser
Deputy Director of Communications, Latin America and the Caribbean
Climate Change Impact
Less rain and higher temperatures; Extreme climate events; Unpredictable climate patterns and drought; Human displacement; Biodiversity at risk; Health impacts; Economic impact
Most Affected Population
Rural communities, farmers, indigenous peoples, women, children and the elderly
How to Overcome the Crisis
Reduce emissions; adapt to climate change; research and monitor climate; implement sustainable development policies; international cooperation
Seven Effects of Climate Change in Central America
- Less rain and higher temperatures
- Anticipated reductions in rainfall pose a significant threat, leading to potential crises in agriculture and access to drinking water. The region has experienced a notable temperature increase of 1.2ºC (34.7 ºF), intensifying the water demand. This challenge increases with higher maximum and minimum temperatures, along with more days exceeding 40ºC (104 ºF). Nights are also getting warmer.
- Weather-related extreme events
-
Central America is experiencing an escalation in the frequency and intensity of weather-related extreme events due to climate change. Hurricanes, floods, and droughts are becoming more severe, posing a direct threat to food security. These events not only lead to the destruction of harvests but also result in damage to farming soil.
-
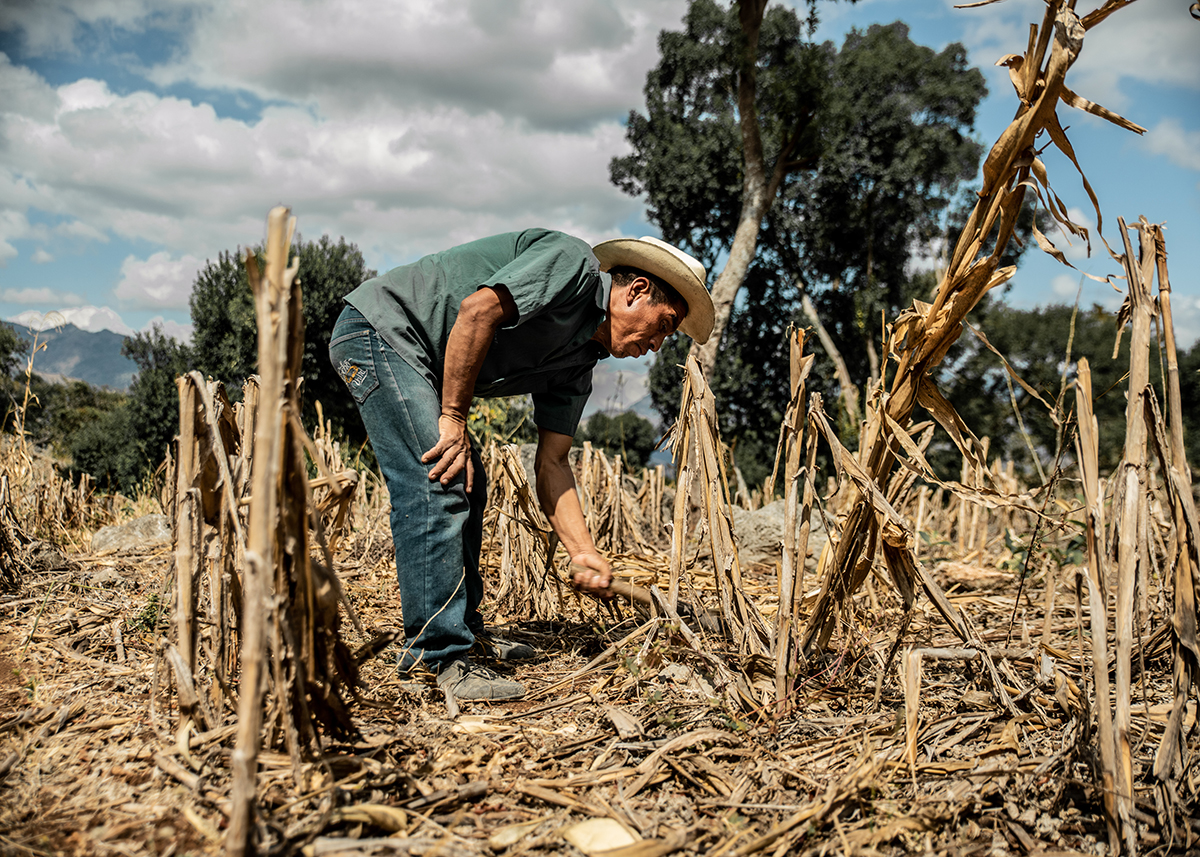

Silverio Méndez is a farmer from Chiquimula, Guatemala. Over the past years, he and his family have been affected by long drought seasons that forced them to find new ways of getting by. Photo by Julian Spath/CRS.
- Unpredictable climate patterns and drought
-
Central America largely relies on subsistence farming. Unpredictable climate patterns and drought, aggravated by climate change, will make the growth of basic foods like maize and beans harder. As a result, food security in the region and the livelihoods of rural communities will be threatened.
-
- Displacement and social conflict
-
Natural disasters and food insecurity are causing people to migrate, both within countries and outside the region, mainly to the U.S. Water scarcity and the higher cost of water will cause social conflict, mainly affecting the most vulnerable and poorest populations.
-

Porfirio and Cristina used to support their household with the income they made from their crops. But when intense drought started to impact their harvests, the couple was forced to go off their farm to find work. Photo by Philip Laubner/CRS.
- Biodiversity at risk
-
Central America is a region rich in biodiversity, with many plant and animal species native to the region. Climate change threatens this biodiversity by altering ecosystems, making specific habitats inappropriate for the species living in them.
-
- Health impact
-
The climate crisis may also have an impact on public health. For example, rising temperatures may cause an increase in mosquito-borne diseases, such as dengue fever and Zika.
-
- Economic impact
-
All of the above impacts of climate change will have consequences for the economy:
-
Governments must spend more resources to respond to natural disasters.
-
People lose their livelihoods.
-
The resulting uncertainty can discourage investment.
-
-
A climate change adaptation approach is necessary to mitigate these effects, including diversification of the economy, implementation of climate-resilient agriculture techniques, and improvement of infrastructure to better deal with natural disasters.

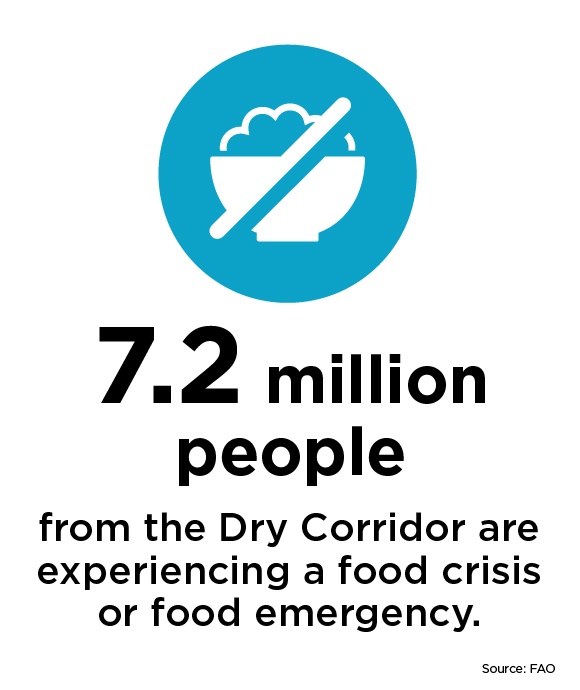
What is the Dry Corridor?
The Central America Dry Corridor is known for its long periods of drought and unpredictable climate patterns. It stretches from Mexico to Costa Rica and crosses through Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
This region has short and irregular rain and long dry seasons. Climate change has worsened these conditions, making this area highly vulnerable to extreme climate events, such as extended drought and flooding.
The Dry Corridor is a region of entrenched poverty with many rural families trying to make a living from subsistence farming where maize and beans are the main crops.
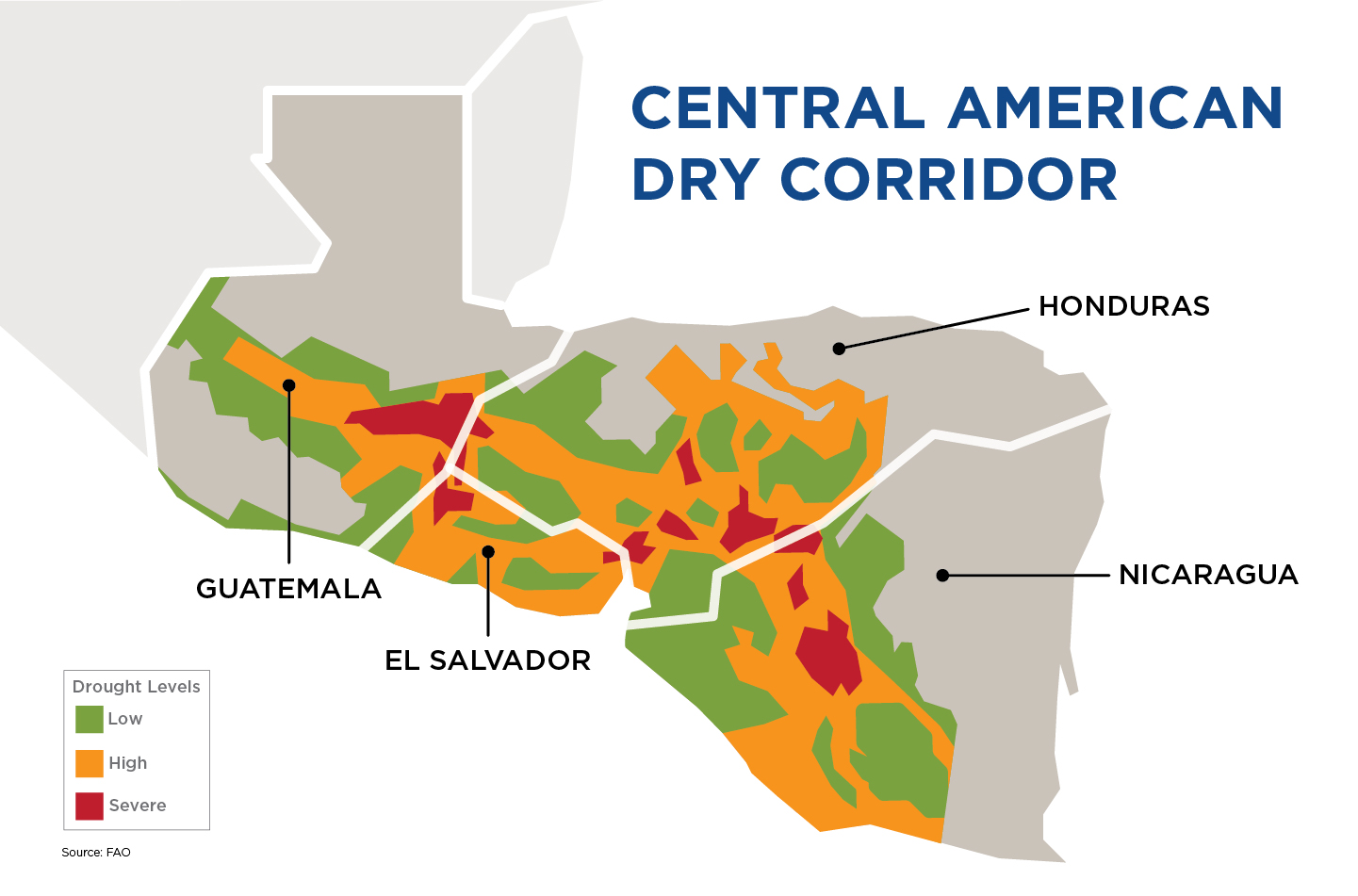
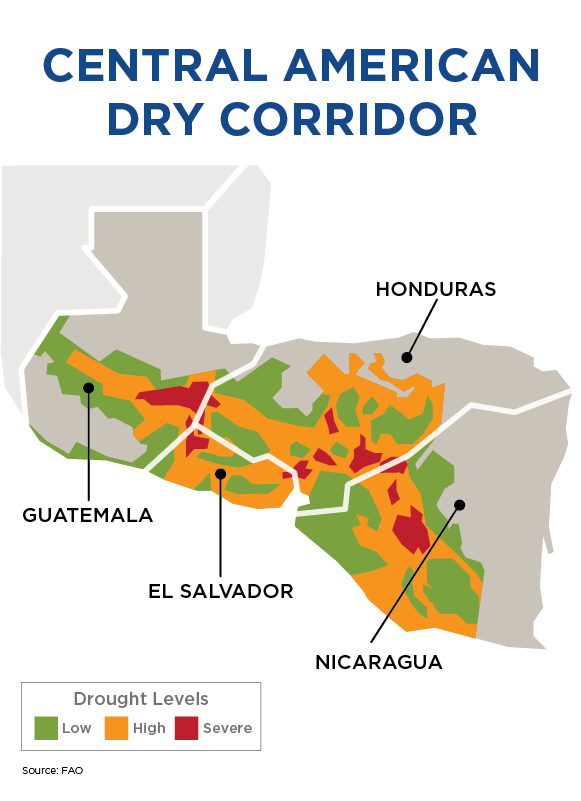
What is the current situation of the Dry Corridor?
The situation in Dry Corridor is critical. The lives of thousands of people are at risk. Unpredictable and extreme weather events have made agriculture more difficult and contribute to food insecurity and malnutrition.
- Approximately 500,000 people suffer from severe food insecurity, especially in Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
- 65% of families in the Dry Corridor do not have any food reserves. To survive, they chose to migrate to urban areas, reduce the portions and frequency of the food they consume, buy cheaper and less varied food, sell their livestock, and resort to taking out loans.
- The permanent drought situation in the Dry Corridor has reduced the region's water supply, making proper hygiene difficult. The absence of basic sanitation can lead to digestive problems and severe malnutrition.
- Due to the lack of economic opportunities, many people from this area are forced to migrate, often to more prosperous regions of Central America or the United States.


Which are the most affected populations?
The climate crisis disproportionately impacts specific populations of the Dry Corridor. These groups lack the necessary resources and support to adapt:
- Rural communities
- Rural communities usually have reduced access to essential drinking water, medical care, and education services. These communities typically rely on agriculture and need to be able to adapt to climate change.
- Subsistence agriculture
- Subsistence farmers depend on crops such as maize and beans to feed their families and generate income. However, extended drought periods and unpredictable rains are making it increasingly challenging to grow these primary crops.
- Indigenous populations
- Indigenous populations often live in marginalized communities and face challenges such as discrimination and lack of access to essential services. This makes them especially vulnerable to climate change.
- Women
- Women are usually responsible for collecting water and food for their families. Climate change can make these tasks more challenging, and women often have to work harder to ensure family survival. Women need more access to education and economic resources to better adapt to climate change.
- Children and the elderly
- Children and the elderly are especially vulnerable to the effects of the climate crisis. Children can suffer from malnutrition and diseases when families cannot grow enough food. The elderly can be more vulnerable to heat-related sickness. And water-borne illnesses.


Climate change is a complex global challenge requiring coordinated efforts on many fronts. In the case of Central America, several strategies can help the region adapt to the climate crisis and alleviate its effects:
- It threatens food production. Climate change substantially impacts agriculture and affects food security in the region. More intense rains during the wet season and more severe droughts in the dry season can threaten food production.
- It destroys crops and agricultural infrastructure. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, destroy crops and agricultural infrastructure and are especially devastating during harvest.
- It increases plagues and diseases. Climate change may alter the distribution and severity of plagues and diseases affecting agriculture. Heat and humidity favor the propagation of plagues and diseases.
- It impoverishes farmers and makes food more expensive. Climate change reduces agricultural production. This impacts the income of farming families and increases food prices which affects people's access to sufficient and nutritious food.
Climate change threatens vital crops in Central America, many of which are essential for the region's economy or are part of the basic diet of its population.
Coffee, maize, beans, plantain and banana, cocoa, and rice are at risk due to rising temperatures, extended drought, water shortages, and natural disasters.

Maize of different colors is becoming extinct. Photo by Oscar Leiva/Silverlight for CRS.
Climate change is a complex global challenge requiring coordinated efforts on many fronts. In the case of Central America, several strategies can help the region adapt to the climate crisis and alleviate its effects:
- Reducing emissions: It is possible to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved by adopting renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, protecting, and restoring soils and forests, and adopting more sustainable agricultural practices.
- Adapting to climate change: Involves taking measures to face the effects of climate change. This may include building climate-resilient infrastructure, improving early warning systems for natural disasters, implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices, and developing water management plans.
- Investigating and monitoring the weather: Gathering and analyzing climate data helps countries better understand the risks they face and plan accordingly.
- Adopting sustainable development policies and strategies: Countries can reduce their vulnerability to climate change by addressing challenges such as poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, access to water, and food insecurity, among others.
- Regional and international cooperation: Can be vital to addressing climate change, as it is a global issue that does not respect national borders. Cooperation can involve sharing information and best practices, providing financial and technical assistance, and addressing shared challenges.
The international scientific community agrees that we can still avoid the worst effects of climate change if we act quickly and decisively.
We must take action now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and prepare for the changes that are already inevitable.
In Central America, CRS works with small farmers to implement sustainable agricultural practices that will help them adapt to climate change.
Using the Water Smart Agriculture (WSA) program, we are facilitating access to more than 100,000 farmers in Central America and Mexico to soil restoration and water protection practices that enable them to grow more resilient crops while increasing their production and income.

How can you help?
You can help the communities most affected by climate change in Central America to adapt and thrive.
Sign a petition demanding the U.S. Congress provide adequate funding to support the communities most affected by climate change.
How else can you help?
Can you help us to get the word out?
Follow and retweet @catholicRelief and @CRSNews on Twitter for the latest updates.











